

Dosing & Treatment
Follow the recommended
dosing schedule1
Carol, patient living with PBA
At day 8, titrate up to 2 capsules a day1
Efficacy beyond week 1 in the pivotal trial was achieved with q12h dosing.1
NUEDEXTA is a combination of dextromethorphan HBr (20 mg) and quinidine sulfate (10 mg) in a capsule. It can be taken with or without food.1
The need for continued treatment should be reassessed periodically, as spontaneous improvement of Pseudobulbar Affect (PBA) symptoms occurs in some patients.1
HBr=hydrobromide; po=orally; q12h=every 12 hours; qd=once daily.
Dosage and administration in specific populations
In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. No dose adjustments are required in patients with mild to moderate renal or hepatic impairment. NUEDEXTA has not been evaluated in patients with severe renal or hepatic impairment; however, increases in dextromethorphan and/or quinidine levels are likely to be observed.1
NUEDEXTA can help reduce PBA episodes.1 Hear stories from some patients


[On NUEDEXTA, my mom] is living her life with fewer PBA episodes.Caregiver of a patient living with PBA
NUEDEXTA is a central nervous system (CNS) agent that is categorized in the “Central Nervous System, Other” pharmacologic class in the United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary (USP–NF). NUEDEXTA is not an antipsychotic medication or a controlled substance.1
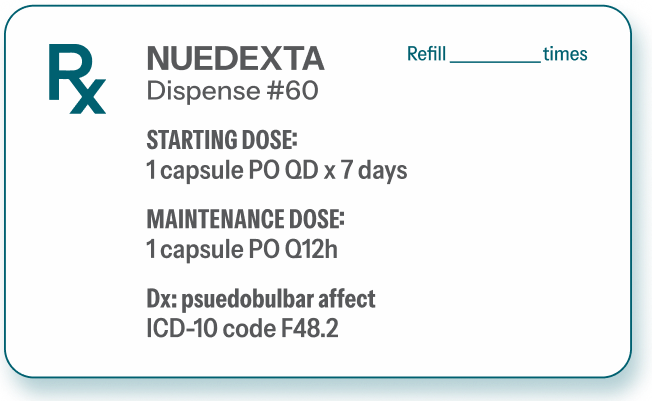
Script pad is used for illustrative purposes only.
PBA is a separate neurologic diagnosis, and the right diagnosis can lead to the right treatment.2
ICD-10 diagnosis codes are provided for informational purposes only and do not guarantee that billing codes will be appropriate or that coverage and reimbursement will result.3
Providers should consult with their payers for all relevant coverage, coding, and reimbursement requirements. It is the sole responsibility of the provider to select proper codes and ensure the accuracy of all claims used in seeking reimbursement.
This resource is not intended as legal advice or as a substitute for a provider’s independent professional judgment.

Script pad is used for illustrative purposes only.
-
References:
1.
Nuedexta. Package insert. Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.; 2022.
-
2.
Brooks BR, Crumpacker D, Fellus J, Kantor D, Kaye RE. PRISM: a novel research tool to assess the prevalence of pseudobulbar affect symptoms across neurological conditions. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e72232. doi:10.1371/
journal.pone.0072232 -
3.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ICD-10-CM tabular list of diseases and injuries. Accessed June 10, 2024. https://ftp.cdc.gov/
pub/ health_statistics/ nchs/ publications/ ICD10CM/ 2022/ icd10cm-tabular-2022-April-1.pdf
Copay savings card
Share this card with your eligible patients to help them save on their NUEDEXTA prescription and refills.
10-day sample
Eligible healthcare providers can request a free 10-day sample of NUEDEXTA for appropriate patients.
